Pregnancy is a miraculous journey filled with anticipation and excitement, but it also involves numerous complexities and considerations for the health of both the mother and the baby. One critical factor that often comes into play is the Rh factor, a component of blood that can significantly impact pregnancy outcomes. In this article, we’ll explore what the Rh factor is, why it matters during pregnancy, and how medical professionals manage potential complications associated with Rh incompatibility.
What is the Rh factor?
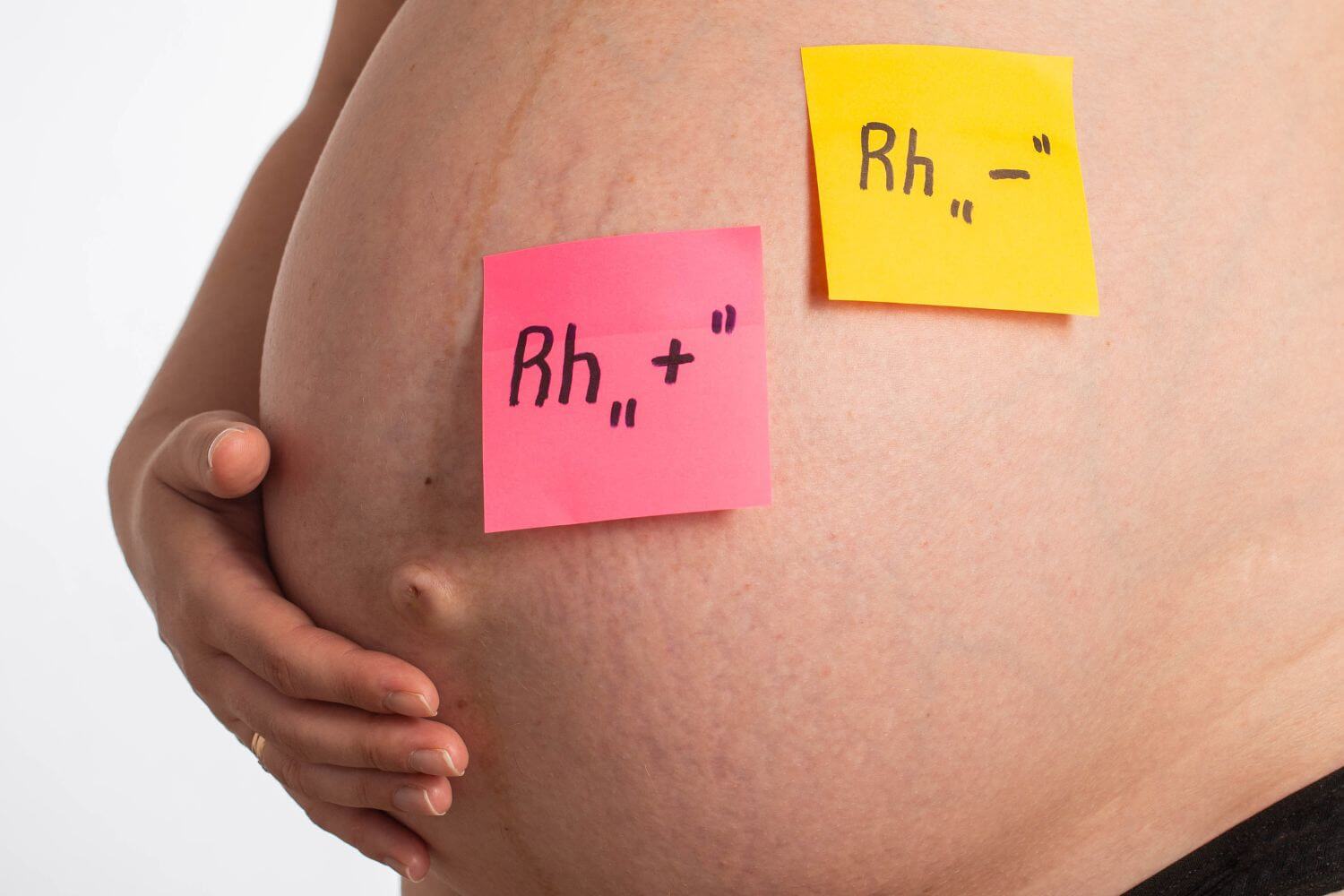
The Rh factor, short for Rhesus factor, is a protein that can be present on the surface of red blood cells. Individuals are classified as Rh-positive if they have this protein and Rh-negative if they lack it. The Rh factor is inherited, with its presence or absence determined by genetics.
Rh factor in pregnancy is relevant when the blood of the mother and baby may come into contact. If an Rh-negative mother is carrying an Rh-positive baby, and there is mixing of blood during pregnancy or delivery, the mother’s immune system may recognize the baby’s Rh-positive blood cells as foreign and produce antibodies against them. This situation is known as Rh incompatibility.
Why Does Rh Incompatibility Matter?
Rh incompatibility can lead to a condition called Rh disease or hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN). In subsequent pregnancies with Rh-positive babies, the mother’s antibodies may cross the placenta and attack the baby’s red blood cells, potentially causing severe complications such as anemia, jaundice, and, in extreme cases, brain damage or stillbirth.
What Can Be Done About Rh Incompatibility?
To prevent Rh-related complications, medical professionals take proactive measures. One common intervention is the administration of Rh immunoglobulin (RhIg) to Rh-negative pregnant women. RhIg, commonly known as the Rh shot, is given around 28 weeks of gestation and within 72 hours of childbirth or any situation where there is a risk of Rh-positive blood mixing with Rh-negative blood. This injection helps prevent the mother’s immune system from producing antibodies against Rh-positive blood cells.
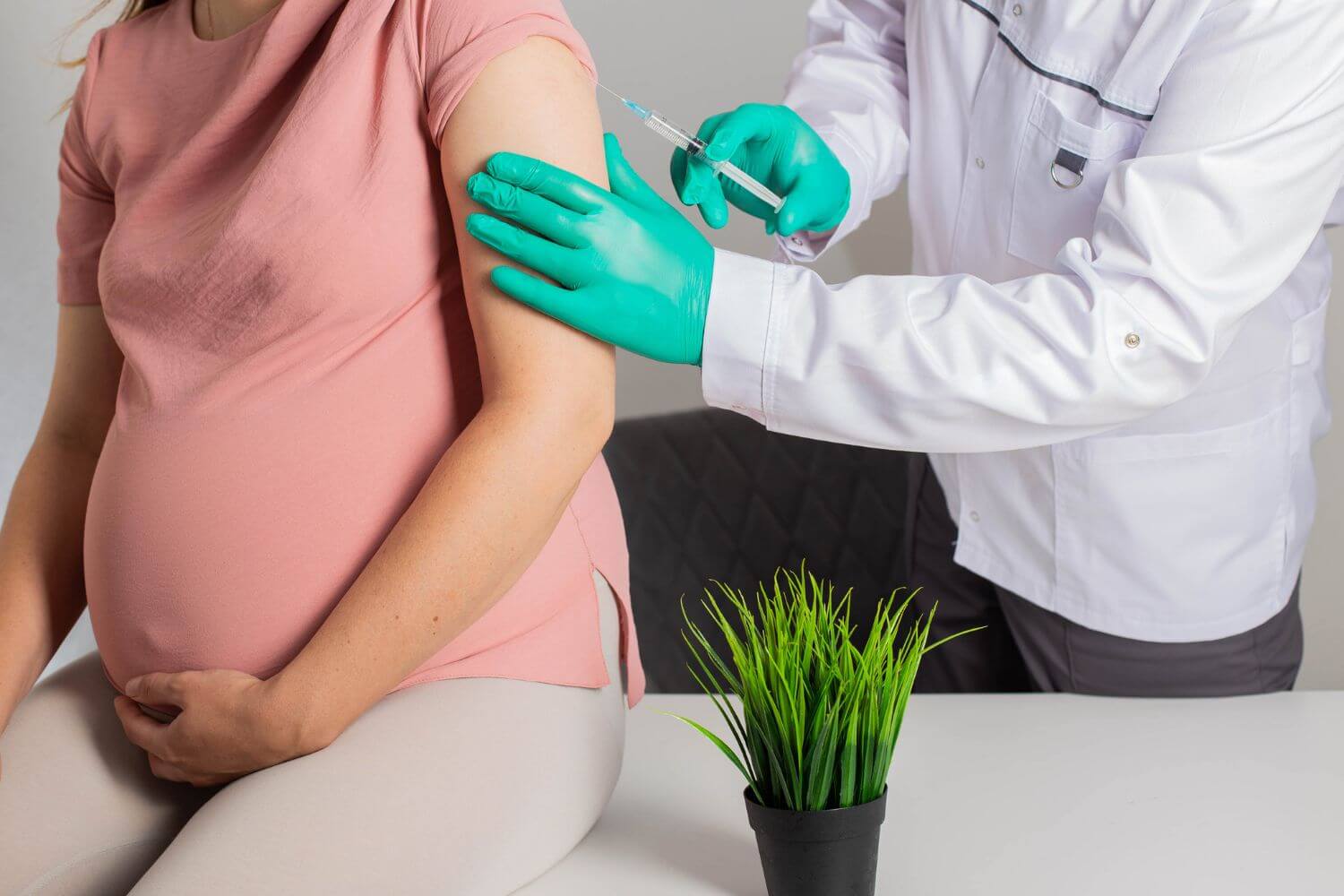
Throughout pregnancy, healthcare providers monitor Rh-negative mothers for the development of antibodies. If antibodies are detected, additional monitoring and interventions may be necessary to ensure the well-being of the baby. Advanced medical technologies and interventions, such as intrauterine blood transfusions, may be employed in severe cases to manage Rh-related complications.
Understanding Rh Factor is Crucial
Understanding the Rh factor and its implications during pregnancy is crucial for ensuring the health and well-being of both the mother and the baby. Advances in medical science, particularly in the field of obstetrics, have provided effective ways to manage Rh incompatibility and minimize potential risks. Regular prenatal care, early detection of Rh incompatibility, and timely interventions such as RhIg administration are key components of ensuring a healthy pregnancy for Rh-negative mothers carrying Rh-positive babies. By raising awareness about the importance of Rh factor in pregnancy, we empower expectant parents to make informed decisions and enable healthcare professionals to provide the best possible care for a safe and successful pregnancy journey.